Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery With Retroesophageal Course
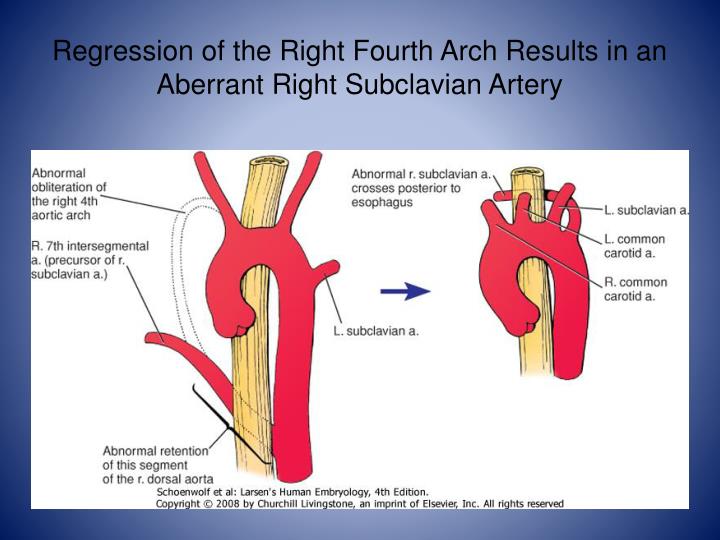
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery With Retroesophageal Course - An aberrant right subclavian artery is the most common of the aortic arch anomalies. Aberrant right subclavian arteries are the commonest of the aortic arch anomalies. Aberrant right subclavian artery means that instead of being the first branch, the right subclavian artery arises on its own as the fourth branch, after the left subclavian artery. Aberrant right subclavian arteries, also known as arteria lusoria, are one of the commonest aortic arch anomalies. The lusorial artery (aberrant right subclavian artery) is an anatomical variation in which the brachiocephalic trunk (innominate artery) is not present and, therefore, the subclavian artery originates directly from the aortic arch, running in a posterior course that can cause contact with the esophagus and trachea 1,2,3. It then hooks back posterior to esophagus to reach the right side. Moreover, the recurrent laryngeal nerve does not follow the orthodox course, which is important in thyroid and parathyroid surgeries 6. A bulbous enlargement of the proximal segment of the aberrant right subclavian artery at its origin from the aortic arch is also demonstrated suggestive of kommerell diverticulum. The aberrant right subclavian artery travels posterior to the esophagus, which appears on an upper gi study as a posterior smooth esophageal indentation. In our case, the aberrant right subclavian artery passes behind the esophagus and trachea which account about 80% in this type of vascular anomaly. Aberrant right subclavian artery means that instead of being the first branch, the right subclavian artery arises on its own as the fourth branch, after the left subclavian artery. A bulbous enlargement of the proximal segment of the aberrant right subclavian artery at its origin from the aortic arch is also demonstrated suggestive of kommerell diverticulum. The aberrant right subclavian artery travels posterior to the esophagus, which appears on an upper gi study as a posterior smooth esophageal indentation. The lusorial artery (aberrant right subclavian artery) is an anatomical variation in which the brachiocephalic trunk (innominate artery) is not present and, therefore, the subclavian artery originates directly from the aortic arch, running in a posterior course that can cause contact with the esophagus and trachea 1,2,3. It then hooks back posterior to esophagus to reach the right side. Moreover, the recurrent laryngeal nerve does not follow the orthodox course, which is important in thyroid and parathyroid surgeries 6. The right subclavian artery, right axillary and right brachial artery are patent. Patients with aberrant right subclavian artery are almost asymptomatic and usually seen incidentally, but some patients could come with dysphagia ( dysphagia lusoria). In our case, the aberrant right subclavian artery passes behind the esophagus and trachea which account about 80% in this type of vascular anomaly. An aberrant right subclavian artery is the most common of the aortic arch anomalies. Patients with aberrant right subclavian artery are almost asymptomatic and usually seen incidentally, but some patients could come with dysphagia ( dysphagia lusoria). Moreover, the recurrent laryngeal nerve does not follow the orthodox course, which is important in thyroid and parathyroid surgeries 6. In our case, the aberrant right subclavian artery passes behind the esophagus and trachea which account about. Aberrant right subclavian artery means that instead of being the first branch, the right subclavian artery arises on its own as the fourth branch, after the left subclavian artery. The aberrant right subclavian artery travels posterior to the esophagus, which appears on an upper gi study as a posterior smooth esophageal indentation. Patients with aberrant right subclavian artery are almost. A bulbous enlargement of the proximal segment of the aberrant right subclavian artery at its origin from the aortic arch is also demonstrated suggestive of kommerell diverticulum. The right subclavian artery, right axillary and right brachial artery are patent. Aberrant right subclavian artery means that instead of being the first branch, the right subclavian artery arises on its own as. Aberrant right subclavian arteries are the commonest of the aortic arch anomalies. In our case, the aberrant right subclavian artery passes behind the esophagus and trachea which account about 80% in this type of vascular anomaly. The lusorial artery (aberrant right subclavian artery) is an anatomical variation in which the brachiocephalic trunk (innominate artery) is not present and, therefore, the. Aberrant right subclavian arteries are the commonest of the aortic arch anomalies. A bulbous enlargement of the proximal segment of the aberrant right subclavian artery at its origin from the aortic arch is also demonstrated suggestive of kommerell diverticulum. Moreover, the recurrent laryngeal nerve does not follow the orthodox course, which is important in thyroid and parathyroid surgeries 6. The. The aberrant right subclavian artery travels posterior to the esophagus, which appears on an upper gi study as a posterior smooth esophageal indentation. Aberrant right subclavian artery means that instead of being the first branch, the right subclavian artery arises on its own as the fourth branch, after the left subclavian artery. Aberrant right subclavian arteries, also known as arteria. They are often asymptomatic and incidentally discovered as demonstrated in this case. Patients with aberrant right subclavian artery are almost asymptomatic and usually seen incidentally, but some patients could come with dysphagia ( dysphagia lusoria). An aberrant right subclavian artery is the most common of the aortic arch anomalies. The right subclavian artery, right axillary and right brachial artery are. In our case, the aberrant right subclavian artery passes behind the esophagus and trachea which account about 80% in this type of vascular anomaly. It then hooks back posterior to esophagus to reach the right side. They are often asymptomatic and incidentally discovered as demonstrated in this case. Aberrant right subclavian arteries are the commonest of the aortic arch anomalies.. It then hooks back posterior to esophagus to reach the right side. Moreover, the recurrent laryngeal nerve does not follow the orthodox course, which is important in thyroid and parathyroid surgeries 6. The lusorial artery (aberrant right subclavian artery) is an anatomical variation in which the brachiocephalic trunk (innominate artery) is not present and, therefore, the subclavian artery originates directly. In our case, the aberrant right subclavian artery passes behind the esophagus and trachea which account about 80% in this type of vascular anomaly. The right subclavian artery, right axillary and right brachial artery are patent. They are often asymptomatic and incidentally discovered as demonstrated in this case. A bulbous enlargement of the proximal segment of the aberrant right subclavian. A bulbous enlargement of the proximal segment of the aberrant right subclavian artery at its origin from the aortic arch is also demonstrated suggestive of kommerell diverticulum. It then hooks back posterior to esophagus to reach the right side. The right subclavian artery, right axillary and right brachial artery are patent. The lusorial artery (aberrant right subclavian artery) is an anatomical variation in which the brachiocephalic trunk (innominate artery) is not present and, therefore, the subclavian artery originates directly from the aortic arch, running in a posterior course that can cause contact with the esophagus and trachea 1,2,3. They are often asymptomatic and incidentally discovered as demonstrated in this case. Aberrant right subclavian arteries, also known as arteria lusoria, are one of the commonest aortic arch anomalies. Patients with aberrant right subclavian artery are almost asymptomatic and usually seen incidentally, but some patients could come with dysphagia ( dysphagia lusoria). In our case, the aberrant right subclavian artery passes behind the esophagus and trachea which account about 80% in this type of vascular anomaly. Aberrant right subclavian artery means that instead of being the first branch, the right subclavian artery arises on its own as the fourth branch, after the left subclavian artery. Aberrant right subclavian arteries are the commonest of the aortic arch anomalies.Development of an aberrant right subclavian artery (ARSA) and... Download Scientific Diagram
Figure 4 from Aberrant right subclavian artery encountered during debridement of T2
Angiogram the aberrant right subclavian artery and its course... Download Scientific Diagram
PPT Human Embryology Heart Development II PowerPoint Presentation ID140463
Diagrammatic representation of aberrant right subclavian artery (ARSA)... Download Scientific
An aberrant right subclavian artery depicted with aneurysmal dilatation Download Scientific
Association of aberrant subclavian arteries with aortic pathology and proposed classification
Four subtypes with 5 branches. ARSA aberrant right subclavian artery,... Download Scientific
Four subtypes with 5 branches. ARSA aberrant right subclavian artery,... Download Scientific
Illustration of the Distal Origin of the Aberrant Right Subclavian... Download Scientific Diagram
An Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery Is The Most Common Of The Aortic Arch Anomalies.
The Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery Travels Posterior To The Esophagus, Which Appears On An Upper Gi Study As A Posterior Smooth Esophageal Indentation.
Moreover, The Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Does Not Follow The Orthodox Course, Which Is Important In Thyroid And Parathyroid Surgeries 6.
Related Post: