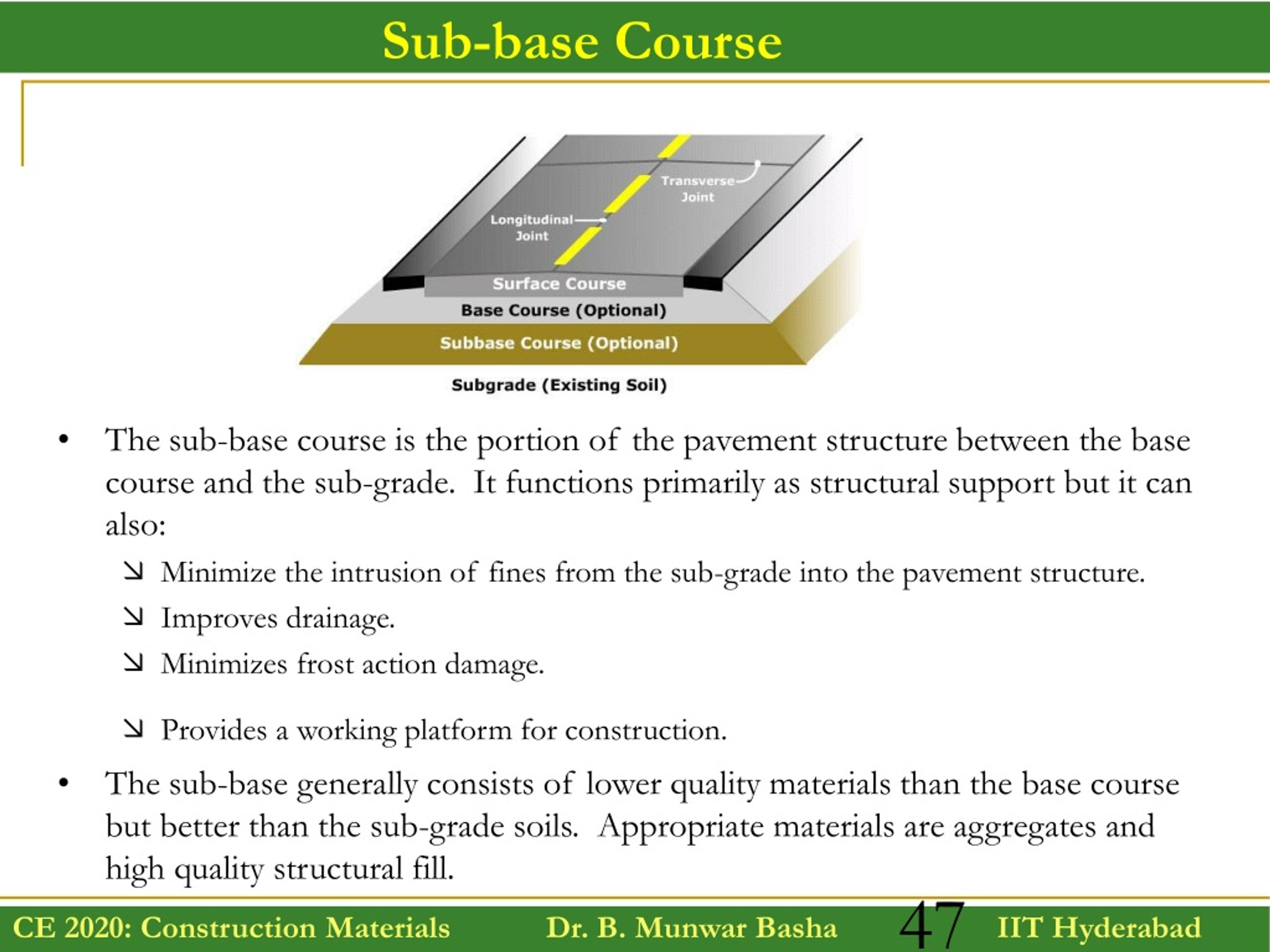
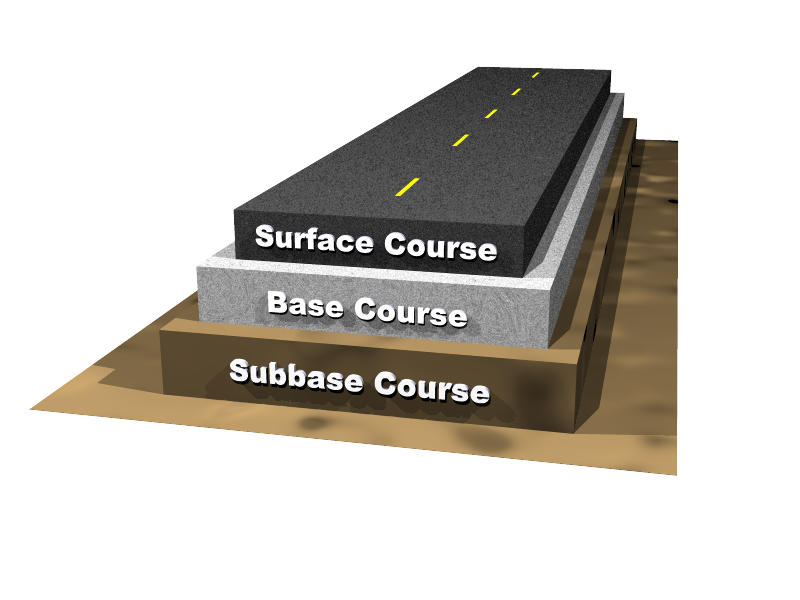
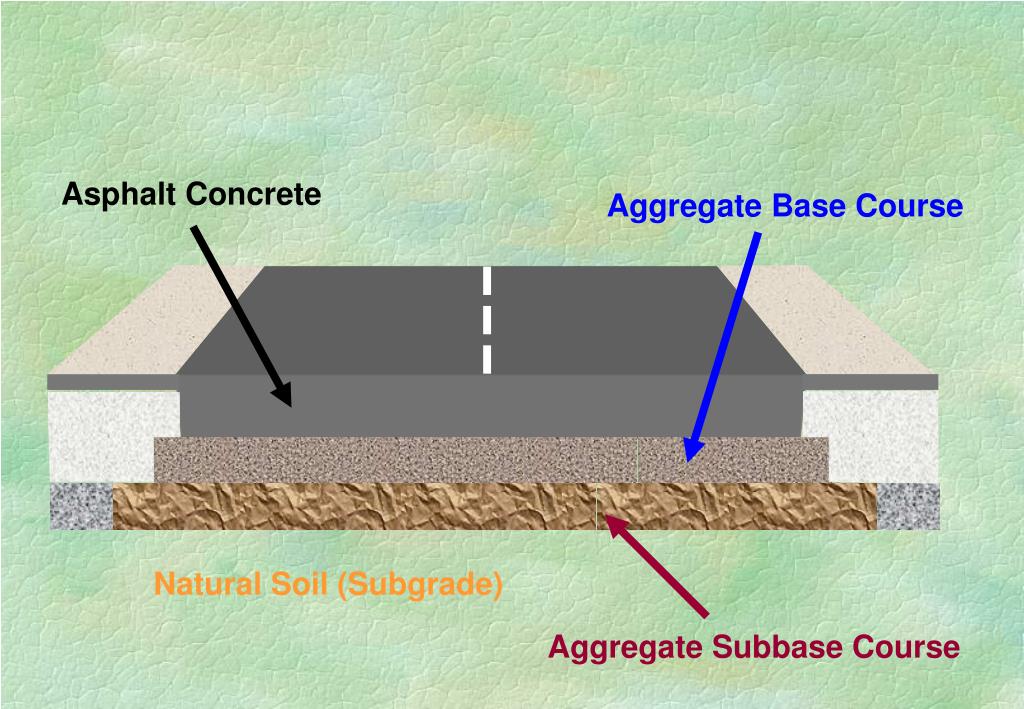
Base Course Vs Sub Base
Base Course Vs Sub Base - The composition and structure of flexible pavement consists of surface course, binder course, base course, subbase course, frost protection course, subgrade. In this video we will see what is the basic difference between subbase & base course. Strictly speaking, however, a base course is a layer of material beneath an asphalt surface; It may be omitted when there will be only foot traffic on the. This document provides specifications for subgrade, subbase, and. Â ¢ with the aggregate base layer functioning. A subbase is not often used. It is located under the surface layer consisting of the. Road structure cross section is composed of the following components: The base course or basecourse in pavements is a layer of material in an asphalt roadway, race track, riding arena, or sporting field. The composition and structure of flexible pavement consists of surface course, binder course, base course, subbase course, frost protection course, subgrade. Road structure cross section is composed of the following components: The bases and subbases for concrete pavements course satisfies one (1) hour of professional development. In a pavement structure, the granular base and subbase are compacted aggregate layers between the asphalt concrete or the portland cement concrete. Â ¢ with the aggregate base layer functioning. In practice, subbase layers are commonly referred to as base courses. It may be omitted when there will be only foot traffic on the. Serves as the foundation and provides uniform. The course is designed as a distance learning course that presents an overview. Acts as the foundational layer, providing uniform. Road pavement consists of four primary layers: The base course or basecourse in pavements is a layer of material in an asphalt roadway, race track, riding arena, or sporting field. Strictly speaking, however, a base course is a layer of material beneath an asphalt surface; In highway engineering, subbase is the layer of aggregate material laid on the subgrade, on. The base course or basecourse in pavements is a layer of material in an asphalt roadway, race track, riding arena, or sporting field. These courses tend to conform to the same shape. Road structure cross section is composed of the following components: The bases and subbases for concrete pavements course satisfies one (1) hour of professional development. A subbase is. The composition and structure of flexible pavement consists of surface course, binder course, base course, subbase course, frost protection course, subgrade. Although the terms “base” and “subbase” are sometimes used interchangeably to refer to the subsurface layers of a pavement, base course is typically used in asphalt pavements, primarily. It may be omitted when there will be only foot traffic. The bases and subbases for concrete pavements course satisfies one (1) hour of professional development. Any distortion or displacement in the subgrade of a flexible pavement is reflected in the base course and upward into the surface course. Road structure cross section is composed of the following components: In this video we will see what is the basic difference between. A subbase is not often used. In a pavement structure, the granular base and subbase are compacted aggregate layers between the asphalt concrete or the portland cement concrete. Road pavement consists of four primary layers: In highway engineering, subbase is the layer of aggregate material laid on the subgrade, on which the base course layer is located. Thus, base courses. Road pavement consists of four primary layers: Road structure cross section is composed of the following components: Any distortion or displacement in the subgrade of a flexible pavement is reflected in the base course and upward into the surface course. The course is designed as a distance learning course that presents an overview. Serves as the foundation and provides uniform. The bases and subbases for concrete pavements course satisfies one (1) hour of professional development. Any distortion or displacement in the subgrade of a flexible pavement is reflected in the base course and upward into the surface course. Serves as the foundation and provides uniform. This document provides specifications for subgrade, subbase, and. Â ¢ with the aggregate base layer. The course is designed as a distance learning course that presents an overview. In practice, subbase layers are commonly referred to as base courses. Rigid pavements are typically constructed using a portland cement bound surface layer over one or more support layers over a prepared natural earth subgrade (figure 5). These courses tend to conform to the same shape. Serves. In highway engineering, subbase is the layer of aggregate material laid on the subgrade, on which the base course layer is located. Although the terms “base” and “subbase” are sometimes used interchangeably to refer to the subsurface layers of a pavement, base course is typically used in asphalt pavements, primarily. Road structure cross section is composed of the following components:. Any distortion or displacement in the subgrade of a flexible pavement is reflected in the base course and upward into the surface course. The base course or basecourse in pavements is a layer of material in an asphalt roadway, race track, riding arena, or sporting field. Rigid pavements are typically constructed using a portland cement bound surface layer over one. Serves as the foundation and provides uniform. The bases and subbases for concrete pavements course satisfies one (1) hour of professional development. This document provides specifications for subgrade, subbase, and. In a pavement structure, the granular base and subbase are compacted aggregate layers between the asphalt concrete or the portland cement concrete. A subbase is not often used. It is located under the surface layer consisting of the. Â ¢ with the aggregate base layer functioning. Although the terms “base” and “subbase” are sometimes used interchangeably to refer to the subsurface layers of a pavement, base course is typically used in asphalt pavements, primarily. Rigid pavements are typically constructed using a portland cement bound surface layer over one or more support layers over a prepared natural earth subgrade (figure 5). In practice, subbase layers are commonly referred to as base courses. It may be omitted when there will be only foot traffic on the. Road pavement consists of four primary layers: In highway engineering, subbase is the layer of aggregate material laid on the subgrade, on which the base course layer is located. The composition and structure of flexible pavement consists of surface course, binder course, base course, subbase course, frost protection course, subgrade. Acts as the foundational layer, providing uniform. What is a base or subbase?What Is Road Pavement Types of Road Pavements Flexible Pavement
Preparation of base course and sub base YouTube
What Is Road Pavement Types of Road Pavements Flexible Pavement
PPT Pavement Types PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID333287
Layers of Road Pavement Concrete Slab Diagram
Pavement Structure Pavement Interactive
Typical Layers Of A Flexible Pavement Engineering Discoveries
Every Civil Engineer Must Know About; Subbase VS Base Course Civil
PPT Introduction to Pavement Design Concepts PowerPoint Presentation
What is sub base course in road construction? Green Square
The Course Is Designed As A Distance Learning Course That Presents An Overview.
The Base Course Or Basecourse In Pavements Is A Layer Of Material In An Asphalt Roadway, Race Track, Riding Arena, Or Sporting Field.
Thus, Base Courses Exist Only.
These Courses Tend To Conform To The Same Shape.
Related Post: